PM vs VR vs Hybrid Stepper Motors
Choosing the right stepper motor is essential for achieving optimal performance in precision motion control. The three main types—permanent magnet stepper motor, variable reluctance stepper motor, and hybrid stepper motor—each have distinct characteristics that affect cost, torque, resolution, noise, and more. This article dives into the key differences to help you make an informed decision.
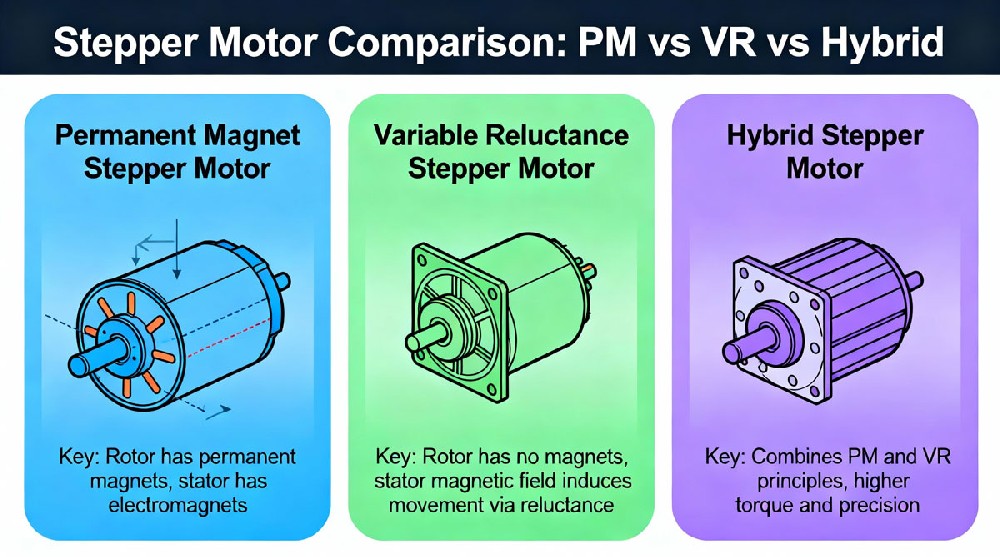
What is a Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor?
A permanent magnet stepper motor utilizes a rotor made from magnetized permanent magnets such as ferrite or NdFeB. Its stator features claw-shaped tooth poles formed by stamping. The motor operates by the interaction of magnetic fields generated by coil currents and the rotor’s permanent magnets, enabling precise stepwise rotation forward or backward. PM stepper motors are known for their moderate cost and reliable torque at low speeds.
How Does a Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor Work?
Variable reluctance (VR) stepper motors differ by having both rotor and stator equipped with toothed poles made from ferromagnetic materials like silicon steel or iron. Unlike PM motors, VR motors lack permanent magnets, so they cannot produce holding or braking torque when stationary. Their operation depends on minimizing magnetic reluctance by aligning the rotor teeth with the stator poles. VR motors tend to be simpler and moderately priced but are noisier and generate more heat.
What Makes Hybrid Stepper Motors Different?
Hybrid stepper motors combine the advantages of both PM and VR types. They feature a rotor with strong NdFeB permanent magnets and toothed rotors and stators with minimal air gaps. The laminated magnetic cores reduce losses and concentrate magnetic flux, providing high precision, strong holding torque, and smooth operation. Hybrid stepper motors typically cost more but offer superior performance including higher resolution and torque.
Top 7 Differences Between PM, VR, and Hybrid Stepper Motors
| Characteristic | Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor | Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor | Hybrid Stepper Motor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Relatively Cheap | Moderate | Relatively Expensive |
| Design Complexity | Moderate | Simple | Complex |
| Step Angle (Resolution) | 3° to 30° | 1.8°, 0.9°, and smaller | 1.8°, 0.9°, and smaller |
| Speed-Torque Curve | High torque at low speed; torque drops significantly at high speed | Less pronounced torque drop at high speed | Highest torque at low speed among three |
| Noise Level | Quiet | Noisy | Quiet (quieter with microstepping) |
| Heat Generation | Low temperature rise | High temperature rise (needs heat sink) | Low temperature rise |
| Microstepping Support | Full, half, and microstepping | Typically full-step only | Full, half, and microstepping |
Why Understanding Stepper Motor Differences Matters
Selecting the right stepper motor type impacts system efficiency, noise levels, precision, and overall cost. For example, if your application requires high torque and precision with smooth operation, a hybrid stepper motor is ideal despite the higher cost. For budget-sensitive projects with simpler needs, a permanent magnet stepper motor offers good value. Variable reluctance motors suit low-cost applications but may suffer from noise and lack of holding torque.
Recommended Articles:
Stepper Motor Step Angle and Calculation Formula: Complete Guide (2025)
Difference Between Sinking Current and Sourcing Current: 7 Powerful Facts
Motor Torque Calculation Formula: Simple Guide with 5 Key Torque Formulas
