Features of Hybrid Stepper Motors
Understanding the features of hybrid stepper motors is essential for selecting the right motor for precision and automation tasks. Hybrid stepper motors combine the benefits of permanent magnet and variable reluctance motors, offering precise control, high torque, and versatile operation. Below are the key features that make hybrid stepper motors a popular choice in various applications.
1. Precise Positioning Control
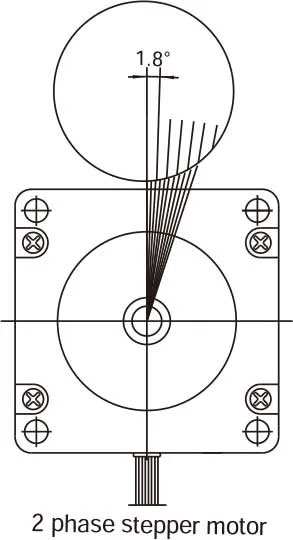
Hybrid stepper motors rotate in fixed step angles, known as the "basic step angle," enabling precise positioning. HDBMOTOR' offers standard 2-phase stepper motors with step angles of 0.9° and 1.8°, and 3-phase motors with 1.2°. Additionally, other step angles like 0.72°, 1.5°, 3.6°, and 3.75° are available on request, allowing customization to meet specific precision requirements.
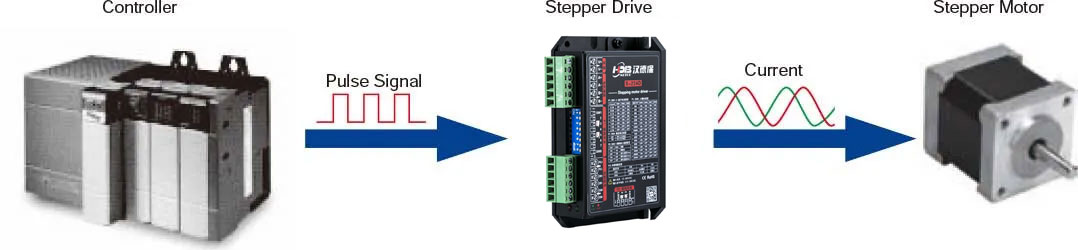
2. Easy Control with Pulse Signals
Control of hybrid stepper motors is straightforward using pulse signals from controllers. Each pulse corresponds to one step of the motor shaft, enabling accurate rotation control. The motor’s rotation angle is directly proportional to the number of pulses received, facilitating simple yet precise motion management.
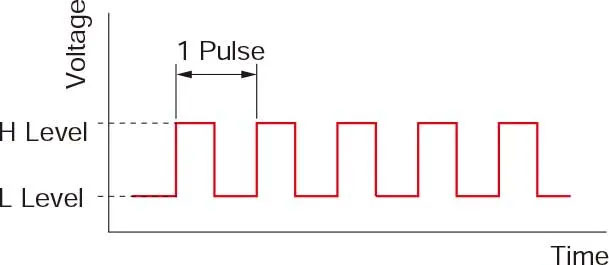
What is a Pulse Signal?
A pulse signal is an electrical signal alternating between ON (high) and OFF (low) states. Each ON/OFF cycle forms a pulse that commands the motor to move one step. This mechanism allows for easy and precise control of motor rotation and speed.
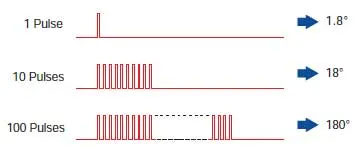
3. The Length of Rotation is Proportional to the Number of Pulses
The rotation distance of the stepping motor is directly proportional to the number of pulse signals (pulse count) applied to the driver. This means the rotation angle of the motor output shaft increases linearly with the pulse count, providing highly predictable and controllable motion.

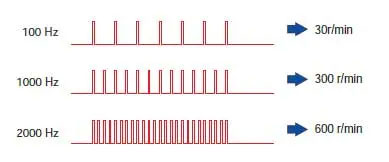
4. Speed Proportional to Pulse Frequency
The speed of a hybrid stepper motor correlates directly with the frequency of the input pulse signals. Increasing pulse frequency increases motor speed, making it simple to adjust velocity by modifying the pulse rate.

5. High Torque in a Compact Size
Hybrid stepper motors deliver high torque despite their compact size. This characteristic offers excellent acceleration and responsiveness, ideal for applications requiring frequent starts and stops. For even higher torque needs at low speeds, geared motor options are available.
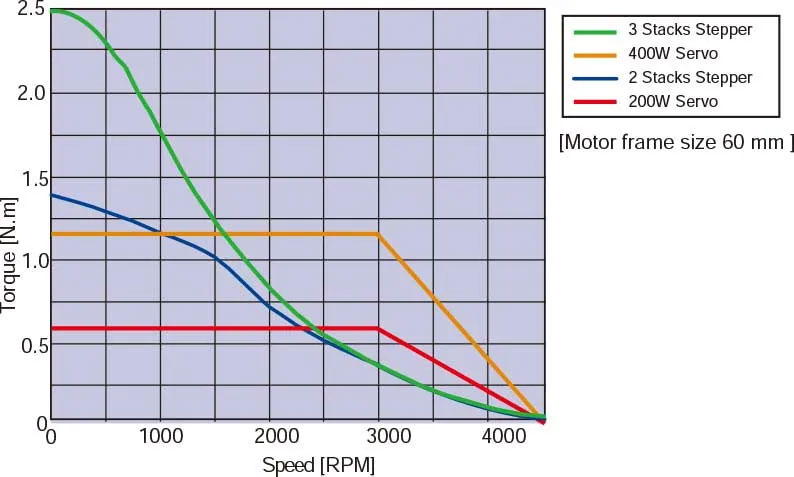
*Frequent Starting/Stopping is Possible *Speed VS Torque Characteristics completion between servo and stepper with same motor size
6. Frequent Starting and Stopping Capability
Unlike many motors, hybrid stepper motors can start and stop frequently without performance loss, making them suitable for precise positioning and indexing tasks.
7. Self-Holding at Stopped Position
When energized, the motor windings provide full holding torque, allowing the motor to maintain its position without the need for a mechanical brake. This feature ensures stable and reliable positioning in many applications.
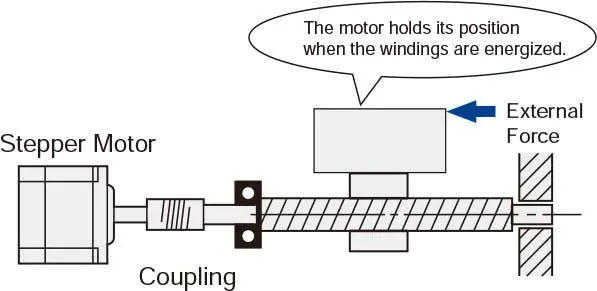
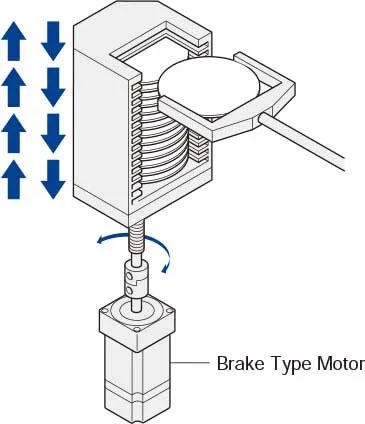
8. Electromagnetic Brake and Closed-Loop Servo Options
In applications requiring vertical operation or holding under external forces, hybrid stepper motors with electromagnetic brakes prevent unintended movement when power is off. Additionally, closed-loop step-servo motors integrate servo control for enhanced efficiency, accuracy, smoothness, and speed.
Recommended Articles:
Stepper Motor Step Angle and Calculation Formula: Complete Guide (2025)
Difference Between Sinking Current and Sourcing Current: 7 Powerful Facts
Motor Torque Calculation Formula: Simple Guide with 5 Key Torque Formulas
