5 Powerful Causes and Solutions for Excessive Motor Vibration
Understanding the causes and solutions for excessive motor vibration is critical for improving stepper motor reliability and extending equipment lifespan. Excessive vibration not only reduces performance but can also lead to premature motor failure. Stepper motors, due to their inherent resonant frequencies, are especially prone to vibration issues if not properly addressed during design and operation.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the common causes of excessive motor vibration and effective electrical and mechanical solutions to mitigate these problems.
Causes of Excessive Motor Vibration
Stepper motors have a mechanical structure that can cause small deviations in rotor position during operation. When the rotor overshoots its target position due to inertia, periodic oscillations occur. If the frequency of these oscillations matches the motor’s natural resonant frequency, resonance happens, often accompanied by noise and potential loss of steps.
Resonance energy exceeding the magnetic holding force between stator and rotor can cause the motor to malfunction. Additionally, phase switching and current fluctuations may exacerbate vibration problems, highlighting the complexity of stepper motor dynamics.
Electrical Methods to Reduce Vibration
1. Adjust Operating Frequency
One direct way to eliminate resonance is by adjusting the operating frequency to avoid the resonant speed range. Although this method can be limited by application requirements, it effectively prevents resonance and improves overall system efficiency.
2. Microstepping Control
Microstepping suppresses vibration by subdividing the motor’s step angle, allowing smoother coil excitation. Unlike full-step operation, where sudden magnetic flux changes cause rotor overshoot, microstepping provides gradual current changes that reduce vibration noise and enhance motion precision.
3. Optimize Drive Current
In low-speed applications such as medical devices or robotic joints, reducing the drive current can stabilize motor operation. Lower current reduces rotor kinetic energy, minimizing overshoot and vibration. However, it’s essential to maintain sufficient torque margins to avoid step loss.
4. Inductance Compensation
Increasing winding inductance can shift or suppress resonance frequencies by modifying the motor’s electrical properties. This reduces the interference caused by AC currents generated during resonance, improving motor stability.
5. Current Decay Optimization
Fast current decay during commutation reduces residual current and torque pulsation, effectively lowering vibration. Experimental data confirm that using fast decay modes significantly improves vibration characteristics.
For technical details on microstepping and current control, refer to Texas Instruments’ motor control guide.
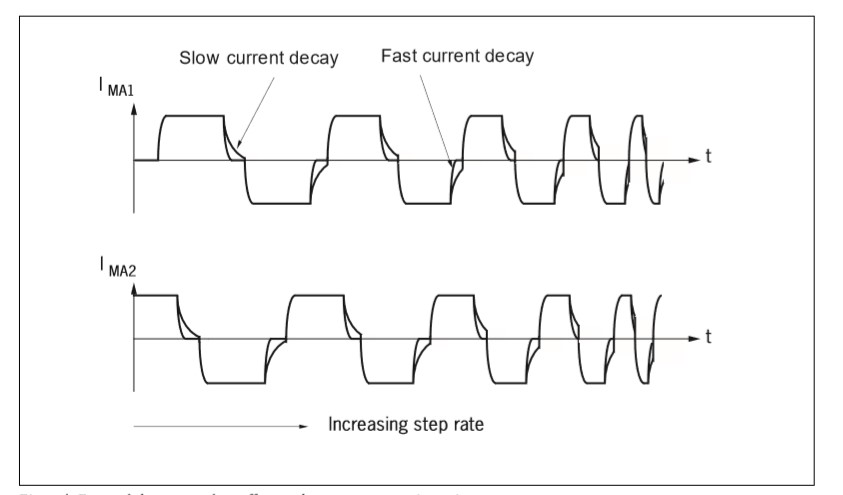
Current Signal from the motor drive
Advanced Winding Techniques to Suppress Resonance
Stepper motors typically use two-phase windings with 90° electrical separation. Traditional phase switching energizes one or two phases alternately, which can cause instability due to inconsistent current distribution.
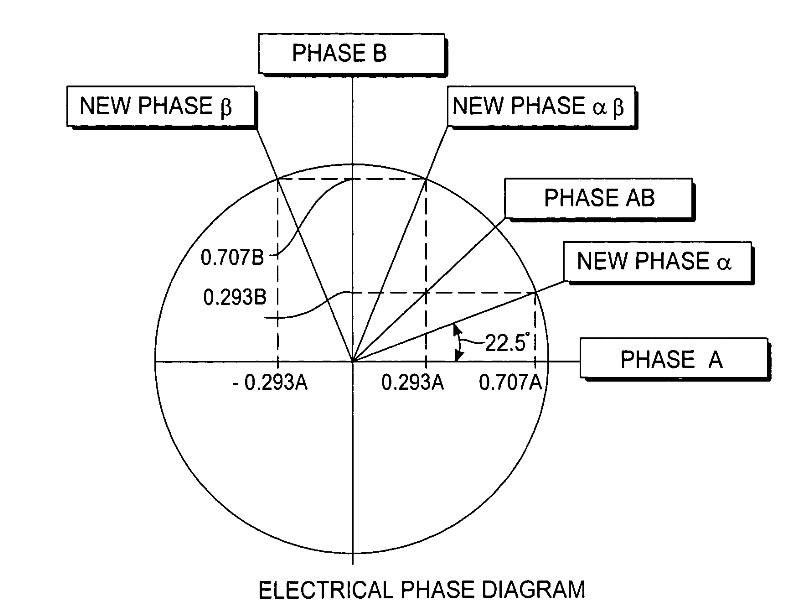
Phase diagram of the R-winding
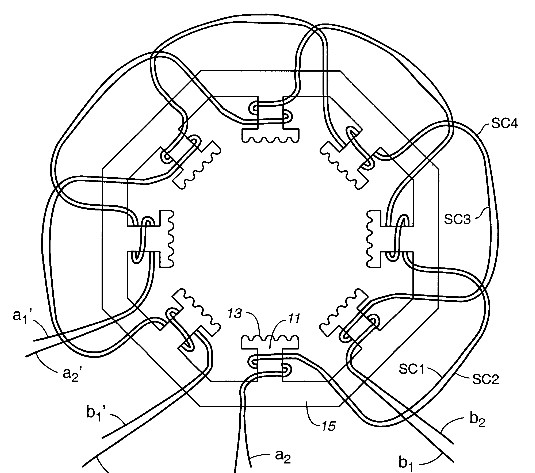
The innovative R-type winding uses two coil sets per pole with a 22.5° electrical phase offset and alternating winding directions. This design enables continuous two-phase energization with a microstepping phase sequence, eliminating single-phase excitation and significantly reducing vibration and noise.
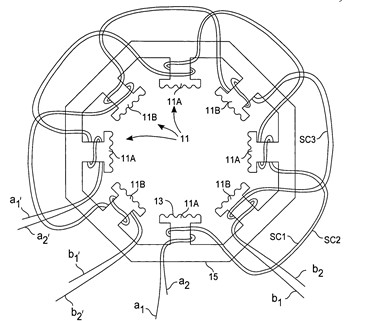
Winding setup of the R-winding
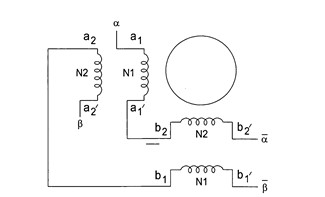
Similarly, the T-type winding connection maintains two-phase continuous energization with inductance characteristics between series and parallel configurations, offering better torque output and stronger torque retention at various speeds.
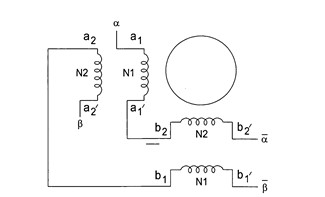
Winding setup of the T-connection
Increasing the number of motor phases, such as using five-phase motors, also reduces vibration by decreasing step angles and excitation energy per step. Combined with microstepping, this approach achieves ultra-fine resolution and minimal vibration.
Mechanical Solutions for Vibration Reduction
Mechanical Dampers
Installing a damper on the motor shaft absorbs vibration energy and increases rotational inertia, stabilizing the system. Flange mounts further enhance vibration absorption by reinforcing the motor structure.
Adjusting Rotor Inertia
Changing rotor inertia by selecting different materials, modifying geometry, or using laminated structures shifts the resonant frequency, reducing vibration amplitude. Increasing rotor length or optimizing rotor design can significantly improve vibration performance.
Air Gap Optimization
Adjusting the air gap between rotor and stator changes torque stiffness and shifts operating points away from resonance zones. This technique helps prevent vibration while maintaining sufficient torque output.
Load Inertia
Adding load inertia effectively increases total system inertia, acting as a mechanical damper and reducing motor vibration amplitude. Proper matching of load and motor inertia is critical for optimal vibration control.
Conclusion
Addressing the causes and solutions for excessive motor vibration requires a coordinated approach combining electrical tuning, advanced winding techniques, and mechanical design optimization. Early consideration during equipment design prevents resonance problems, improves motor accuracy, and extends equipment life.
For customized motor solutions tailored to your application needs, HDBMOTOR’ offers a wide range of advanced stepper motors with proven vibration suppression technologies. Contact HDBMOTOR’ professionals for expert assistance.
Recommended Articles:
What ls A Bipolar Stepper Motor And How Does lt Work
Why ls My Stepper Motor Making A Squealing Noise? 9 Proven Fixes
How To Make A Stepper Motor Rotate According To A Sine Wave Pattern?
