NEMA 17 vs NEMA 23 vs NEMA 34 Stepper Motors
Stepper motors play a vital role in precision motion control across industries such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and automation equipment. Selecting the proper stepper motor model is essential to achieve the desired performance and efficiency. Among the commonly used motors, NEMA 17, NEMA 23, and NEMA 34 sizes dominate due to their versatility and range of torque outputs. This article explains the 7 key differences and typical applications of these motors to guide your selection process.
What is the NEMA Standard?
The National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) is a U.S.-based organization that defines standards primarily for motor mounting dimensions. The numbers in NEMA stepper motors, like 17, 23, and 34, indicate the motor’s flange size in inches — the front face of the motor that mounts onto your equipment.
Size Differences of NEMA 17, NEMA 23, and NEMA 34
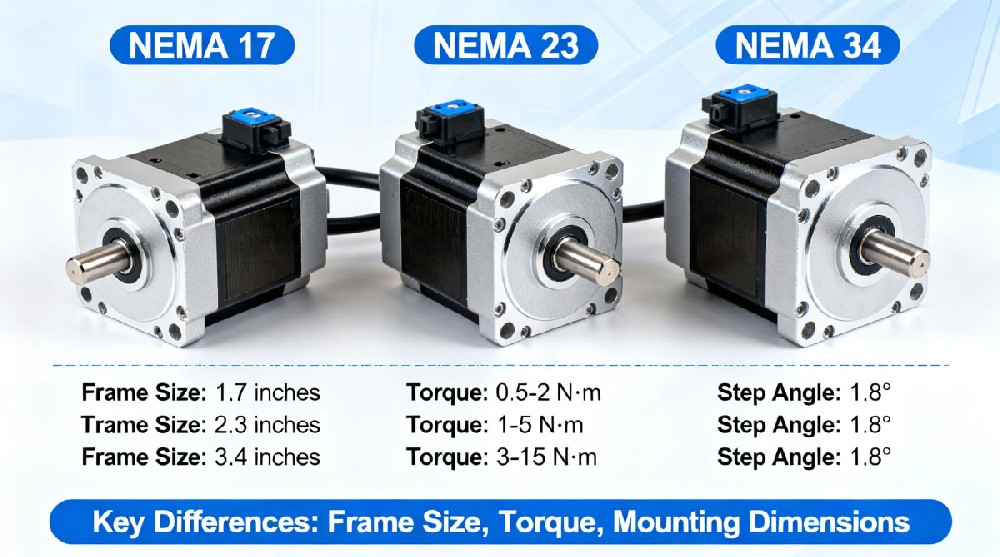
NEMA 17: Flange size of 1.7 inches (approximately 43.2 mm)
NEMA 23: Flange size of 2.3 inches (approximately 58.4 mm)
NEMA 34: Flange size of 3.4 inches (approximately 86.4 mm)
Typically, as the flange size increases, so do the motor’s physical volume, weight, torque, and power output.
Torque and Performance Comparison
NEMA 17: Offers relatively low torque, generally between 0.2 to 0.5 Nm, suitable for light loads demanding high precision, such as 3D printers and desktop automation.
NEMA 23: Provides medium torque, usually 0.5 to 2.0 Nm, ideal for moderate loads including laser cutters, CNC mills, and industrial automation equipment.
NEMA 34: Delivers high torque, typically above 2.0 Nm, designed for heavy-duty industrial applications like large CNC machines and industrial robots.
Typical Applications
NEMA 17
Due to its compact size and precise control, NEMA 17 motors are widely used in 3D printers, photolithography equipment, small robots, and medical devices that require light load handling.
NEMA 23
These motors fit medium-load machines such as laser engravers, CNC routers, and automated assembly lines, making them prevalent in industrial automation.
NEMA 34
NEMA 34 motors are best suited for applications requiring high torque and sustained power, including large CNC machines, industrial robots, and heavy machinery capable of handling substantial loads.
Other Technical Parameters to Consider
Besides flange size and torque, other important factors include step angle, rated current, shaft diameter, and overall weight. These parameters influence the motor’s performance and compatibility with your system. Always review detailed datasheets and consider your specific application requirements before finalizing your choice.
How to Choose the Right Stepper Motor?
Load Requirements: Torque and continuous operating capacity needed for your application.
Space Constraints: Available mounting space and weight limitations.
Precision Needs: Required step angle and motion control accuracy.
Electrical Parameters: Rated voltage, current, and driver compatibility.
Budget: Cost differences among motor sizes and models.
Conclusion
Understanding the key differences between NEMA 17, NEMA 23, and NEMA 34 stepper motors enables you to choose the most suitable motor for your precision motion control needs. By evaluating load demands, space, precision, and budget, you can ensure your system achieves optimal performance and reliability.
Recommended Articles:
Electric Stepper Motor Terminolog
Stepper Motor Selection Parameters: 7 Key Factors You Must Know
