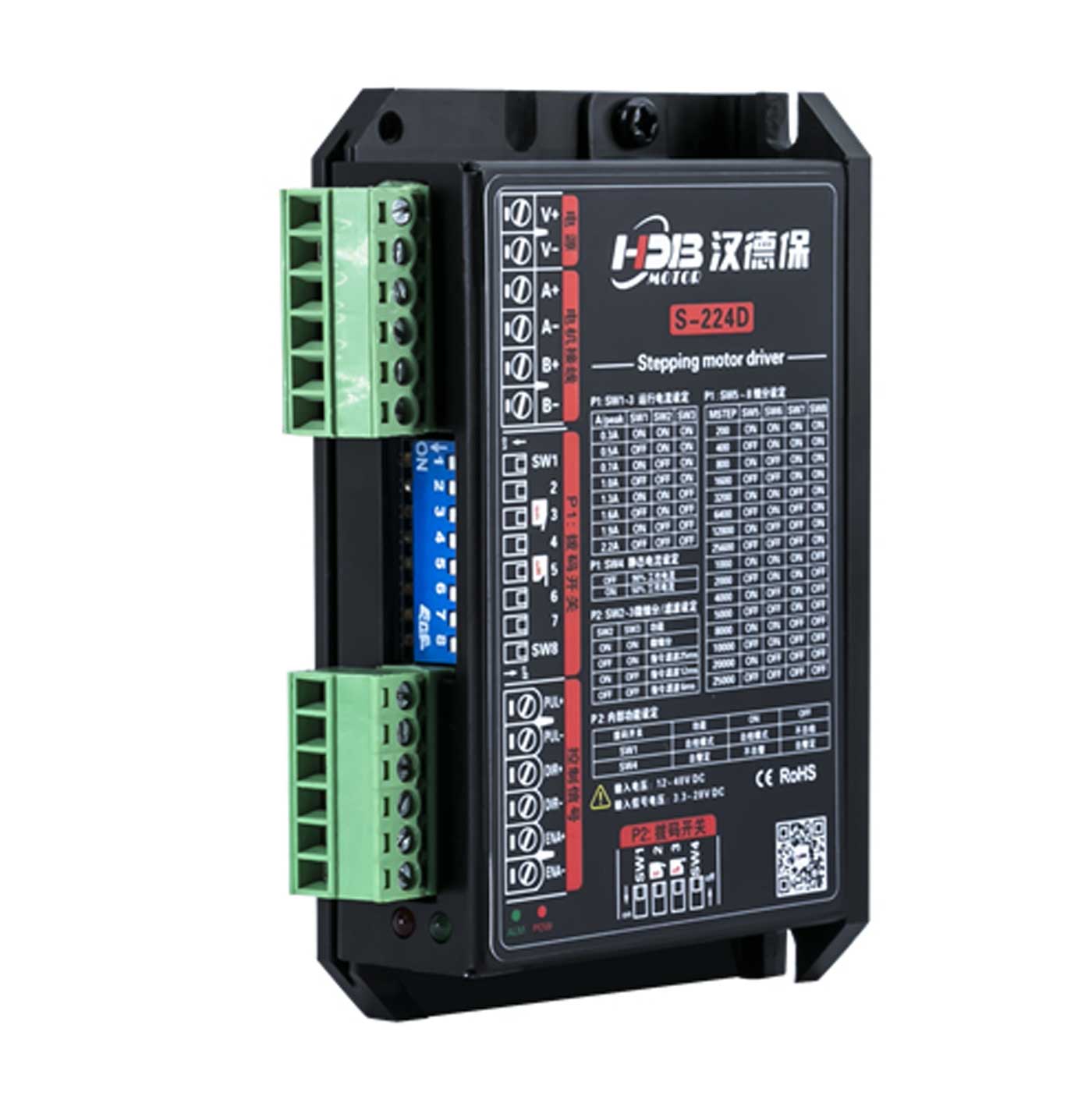
Main Control Chip: Uses a 32-bit DSP chip specially designed for stepper motor control.
Voltage and Current:
Input voltage: 12~48VDC
Output current: 0.3A~2.2A (peak)
Microstepping Settings: 16 levels of microstepping selectable (200~25600 pulses per revolution).
Response Frequency: Pulse response frequency up to 500KHz.
Signal Voltage: Pulse/Direction/Enable signals compatible with 5V~24VDC, no additional current-limiting resistors needed.
Control Modes: Single pulse (Pulse + Direction), Dual pulse (CW/CCW).
Product Self-Test: DIP switch settings for self-test (motor runs repeatedly forward and reverse at 30 RPM).
Resonance Suppression: Automatically calculates resonance points to suppress mid/low frequency vibrations.
Torque Smoothing: Analyzes low-speed torque ripple and cancels corresponding harmonic components to achieve smooth low-speed motion.
Signal Smoothing: Dynamic filtering of speed and direction signals for more stable system performance.
Current Control: PID current control for high-speed, high-torque output with low noise, low vibration, and low heat generation.
System Self-Testing: Automatically detects and matches motor parameters and optimizes motor input current in real time according to load conditions.
Microstepping Interpolation: Reduces vibration during operation and improves running smoothness.
Motor Compatibility: The S-224D two-phase stepper driver is suitable for 4, 6, or 8-wire two-phase stepper motors with an outer diameter of 42mm or less, and rated current between 0.3A and 2.2A.
Generally, the selection of a stepper motor mainly depends on its torque and rated current. Torque is determined by the motor size—larger motors have greater torque. The current mainly depends on inductance; motors with lower inductance have higher current and perform better at high speeds.
Application Fields: Widely used in automation equipment across machinery, electronics, precision instruments, metering devices, medical instruments, etc. Examples include linear slides, electronic devices, optical instruments, laser equipment, security systems, welding machines, dispensing equipment, and automatic assembly devices. It performs especially well in applications requiring low noise and medium to high speed.
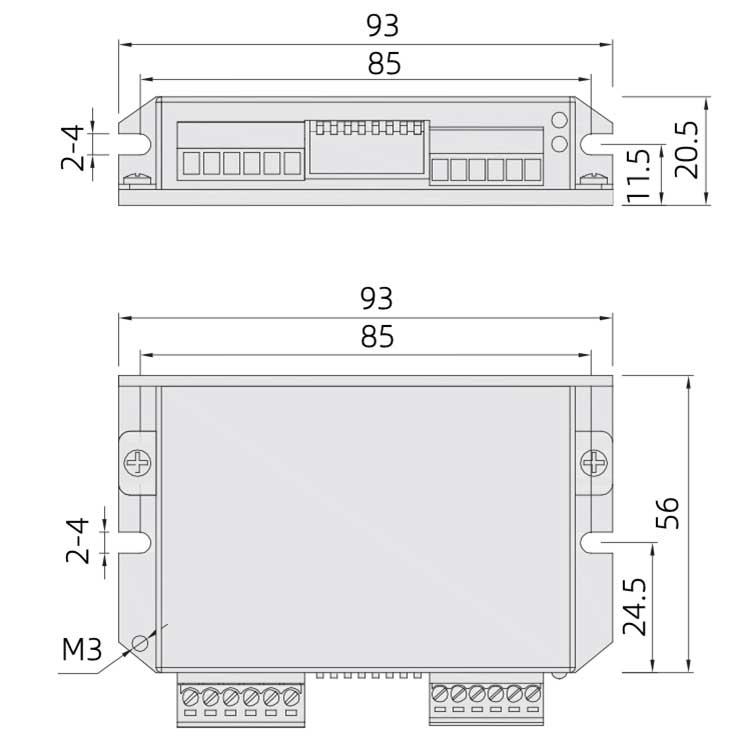
Dimensions
Wiring Instructions
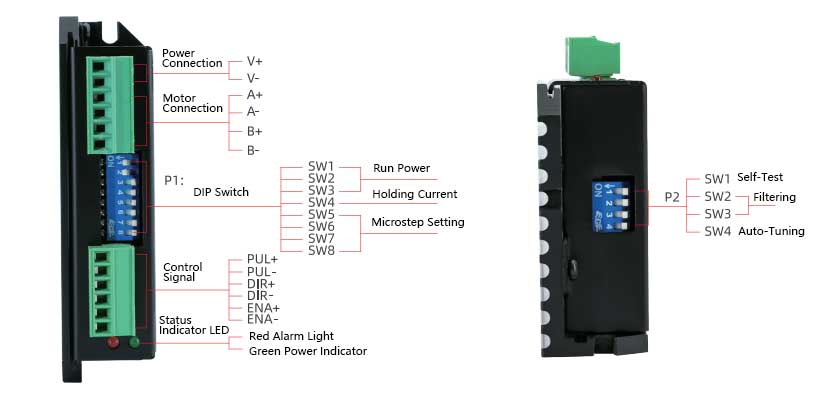
1) Motor and Power Input Terminals
| Terminal Number | Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | V+ | DC Power Input | +12VDC~ +48VDC |
| 2 | V- | Power Ground | 0V |
| 3 | A+ | Phase A Motor Coil + | Swapping the wiring of the same phase coil can change the motor’s rotation direction. For example, swapping the connections of A+ and A-. |
| 4 | A- | Phase A Motor Coil - | |
| 5 | B+ | Phase B Motor Coil + | |
| 6 | B- | Phase B Motor Coil - |
2) Control Signal Terminals
| Terminal Number | Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PUL+ | Pulse Input Positive Terminal | Compatible with DC 5~24V |
| 2 | PUL- | Pulse Input Negative Terminal | Compatible with DC 5~24V |
| 3 | DIR+ | Direction Input Positive Terminal | Compatible with DC 5~24V |
| 4 | DIR- | Direction Input Negative Terminal | Compatible with DC 5~24V |
| 5 | ENA+ | Enable Input Positive Terminal | Compatible with DC 5~24V |
| 6 | ENA- | Enable Input Negative Terminal | Default floating enable |
3) Status Indicators
The green LED is the power indicator. When the driver is powered on, this LED flashes; when the driver is powered off, this LED goes out.
The red LED is the fault indicator. When a fault occurs, this indicator LED flashes periodically; when the fault is cleared by the user, the red LED remains off. The number of red LED flashes represents different fault information, as shown in the table below:
●The red LED ●The green LED
| No. | LED Flash Pattern | Fault Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ● Green LED steady | Driver not enabled | Provide enable signal to driver |
| 2 | ●● Green LED flashing | Driver operating normally | / |
| 3 | ●●●●● 3 red 2 green | Internal voltage error | Increase power supply capacity |
| 4 | ●●●●●4 red 1 green | Driver power input overvoltage | Reduce power supply voltage |
| 5 | ●●●●●●5 red 1 green | Driver overcurrent | Check for short circuit or phase error |
| 6 | ●●●●●●4 red 2 green | Driver power input undervoltage | Increase power supply voltage |
| 7 | ●●●●●●●6 red 1 green | Motor winding open circuit | Connect motor wiring properly |
When the driver encounters a fault, it will stop running and display the corresponding fault code. The user needs to power off and then power on again to clear the fault, or clear the fault via the ENA offline signal and then re-enable the driver. When a fault occurs, the driver saves the latest fault in the EEPROM in a queue format.

